Revision and explanation of Chinese Food Guide Pagoda and Plate (2022)
The Chinese Food Guide Pagoda (2022) and the Chinese Food Guide Plate (2022) depict the main idea and structure of a balanced diet with the graphics of a pagoda and Tai Chi to highlight the Chinese cultural characteristics and concept of balance, and make it easy for the public to remember and understand.
The Chinese Food Guide Pagoda is a graphic representation of the quantity and proportion of various foods intake for an adult according to the key recommendations from Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2022). It follows the principle of a balanced diet and shows the basic food composition in nutrition.
There are five levels on the Pagoda, each of a different size, showing the five categories of food and their amounts. The categories of food include cereals and tubers, fruits and vegetables, meat, poultry, dairy, soybeans, legumes and nuts, cooking oil and salt.
The food quantities are designed according to different energy demand levels. The notes beside the Pagoda indicate the recommended range of daily intake per adult at the energy demand level of 1600~2400 kcal.

Chinese Food Guide Pagoda (2022)
Level 1: Cereals and tubers
Cereals and tubers are the main sources of dietary energy (carbohydrate provides 50%~65% of total energy), and they are also good sources of micronutrients and dietary fiber. It is recommended in the Dietary Guidelines that healthy people over two years old should eat diversified and balanced meals. A total daily intake of 200-300g of cereals, of which whole grains and legumes should make up 50-150g and tubers 50-100g, is recommended.
Cereals, tubers and soybeans are the main sources of carbohydrates. Cereals include wheat, rice, corn, sorghum and their products such as steamed rice, steamed bread, pancakes, bread, and biscuits. Whole grains retain all the components of natural grains. Mixed beans include red beans, mung beans, kidney beans, etc. In China's traditional diet, the common whole grain foods are millet, corn, mung beans, red beans and buckwheat. Therefore, the mixed beans and whole grains are classified into one category. People over two years old should ensure adequate intake of whole grains so as to obtain more nutrients and dietary fiber. Tubers include potatoes and sweet potatoes, which can replace some staple food.
Level 2: Vegetables and fruits
People should eat enough vegetables and fruits, according to the Dietary Guidelines. The recommended daily intake of vegetables is 300g, half of which should be dark-colored, while the daily intake of fresh fruits should be 200-350g.
Vegetables include tender stems, leaves, cauliflower, root vegetables, fresh beans, eggplants, scallions and garlic, and aquatic vegetables. “Dark-colored vegetables” refer to the ones that are dark green, dark yellow, purple, red and similar colors. The nutrients provided by each type of vegetable are different. Dark-colored vegetables are rich in vitamins, phytochemicals and dietary fiber.
There are many kinds of fruits, including kernel fruits (like apples and pears), berries, and citrus, melons and tropical fruits.
Eating fresh fruits is the first choice. However, you can choose some fruit products with low sugar content and pure fruit juice when the supply of fresh fruit is insufficient.
Level 3: Fish, poultry, meat, and eggs
Fish, poultry, meat, and eggs are recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for moderate consumption. Total intake should be targeted at 120-200g on a daily basis.
Fresh animal-based food is a good source of high-quality protein, fat and fat-soluble vitamins. It is suggested that the daily intake of animal-based food should be 40~75g, and consumption of processed meat products should be discouraged.
At present, the meat intake of Chinese Han residents is mainly pork, which contains a lot of fat, so lean meat or poultry should be selected as much as possible.
Common aquatic products include fish, shrimp, crab and shellfish, which are rich in protein, lipids, vitamins and minerals. The recommended daily intake is 40~75g.
Eggs include chicken eggs, duck eggs, goose eggs, quail eggs, and pigeon eggs, as well as their processed products. It is recommended to have one egg per day (equivalent to about 50g), including its yolk. Egg yolk is rich in nutrients such as choline, lecithin, cholesterol, vitamin A, lutein, zinc, and B vitamins.
Level 4: Dairy, soybeans and nuts
Dairy, soybeans and nuts are good sources of protein and calcium with high nutrient density. A wide variety of dairy products should be consumed, and a daily intake equivalent to 300g of liquid milk is recommended.
Soybeans include soya beans, black beans and green beans, and their common products include tofu, soybean milk and dried tofu. Nuts include peanuts, sunflower seeds, walnuts, almonds and hazelnuts. The nutritional value of some nuts is similar to that of soybeans, meaning rich in fatty acids and amino acids. The recommended intake of soybeans and nuts is 25~35g.
Level 5: Cooking oil and table salt
Cooking oil and table salt are indispensable as cooking condiments, but it is better to use them as little as possible. The daily intake of salt and cooking oil for an adult should be less than 5g and 25-30g respectively. According to the recommendations of DRIs (dietary reference intakes), the dietary fat energy supply ratio should account for 35% of the total dietary energy for people aged 1~3 years old; for people over four years old, it should be 20%~30%.
Since other foods also contain fat, consumption of cooking oil needs to be limited on the premise that the recommended amounts of other foods in the balanced diet are met. Cooking oil includes various vegetable oils, such as peanut oil, soybean oil, rapeseed oil, sunflower seed oil, as well as animal oils such as lard, beef tallow and butter.
The consumption of salt is high in China, and salt is closely related to hypertension. Limiting salt intake is a long-term action goal in China. In addition to using less table salt, it is also necessary to control the intake of invisible high-salt food.
Alcohol and added sugar are not a basic part of a daily diet and should be avoided when cooking and eating.
Exercise and water intake
Water is an important part of diet and a necessary substance for all life activities. Its intake is mainly affected by age, physical activity, environmental temperature and other factors. Adults with low levels of physical activity are advised to drink 7-8 cups (1,500-1,700ml) of water daily. The amount of water intake should be appropriately increased at high temperatures or high levels of physical activity. A daily water intake of 2700-3000ml is recommended, where both drinking water and water from diet (including that in food, soup, porridge, milk, etc.) are included.
People should have physical exercise everyday. It is recommended to perform moderate-level physical activities for at least five days per week, accumulating at least 150 minutes in total. Daily activities equivalent to 6,000 steps are also recommended. Energy consumption from low-level physical activity usually accounts for about 1/3 of the total energy consumption, while that of high-level physical activity can be as high as 1/2. To strengthen and maintain energy balance, we need to explore and pay attention to weight changes to find a balance between food intake and exercise.
Chinese Food Guide Plate (2022)
The Chinese Food Guide Plate (2022) shows the food composition and proportion of a person's meals according to the principle of balanced diet.
The plate is divided into four parts, namely, cereal and tubers, animal-based food, soybeans and related products rich in protein, vegetables and fruits. The Plate is intended for people over two years old. Vegetarians can replace meat with beans to obtain sufficient protein.
Compared with the Pagoda, the Plate is more concise. It uses the basic symbols in traditional Chinese culture to show the balance in the Yin and Yang and evolution of all things. On the one hand, it is easier to remember and understand. On the other hand, it also indicates the natural principle of healthy growth and development.
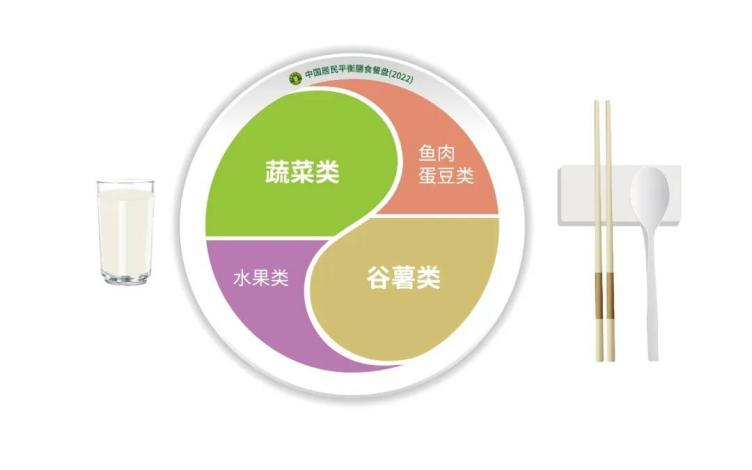
Chinese Food Guide Plate (2022)
Links
>
Copyright© Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. All rights reserved.
京ICP备11024750号-1 京公网安备11011402013004号
京ICP备11024750号-1 京公网安备11011402013004号








